Example: Simple solution
This solution uses a firewall to restrict incoming traffic and a load balancer to balance the traffic between multiple Diffusion™ servers.
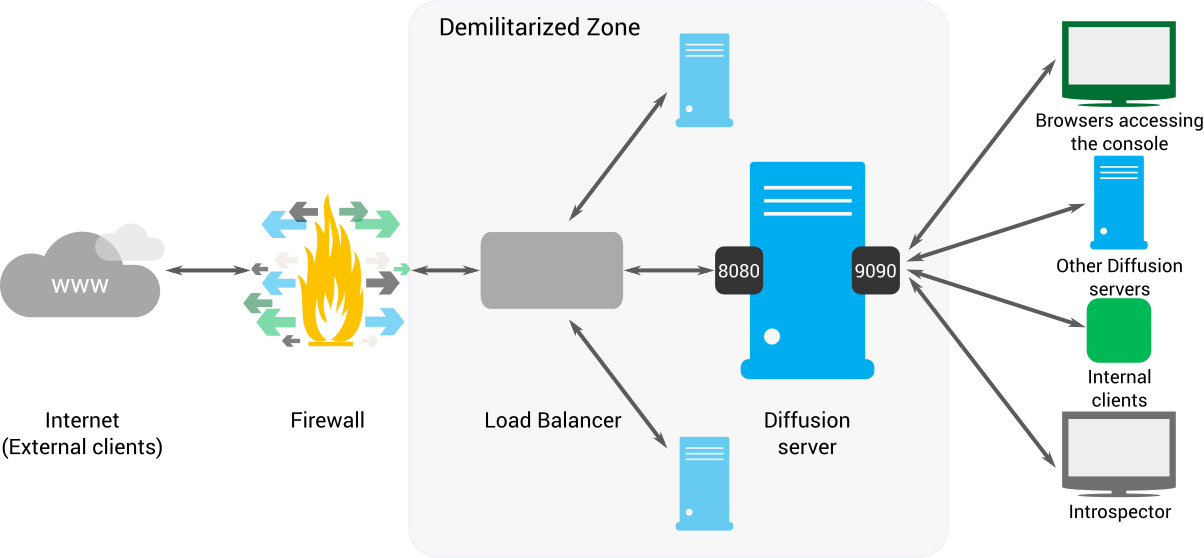
- Client applications can connect to Diffusion from the internet through a firewall.
- The firewall protects the de-militarized zone (DMZ) from unwanted traffic. It allows connections on port 80 and redirects these connections to port 8080.
- The load balancer balances the Diffusion connections between all the Diffusion servers in the DMZ . You can also use the load balancer to filter the URL space and to perform Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) offloading.
- The Diffusion servers receive connections from external clients on port 8080. This port is protected by an authentication handler that performs strict authentication on the incoming connections. Authentication handlers can be local to the server or part of a control client.
- The
Diffusion
servers receive connections from
internal clients on another port, for example 9090. The authentication
controls on this port are less strict because these connections come from
within your network. Internal connections can come from any of the following
components:
- Browsers accessing the Diffusion console
- Internal clients, such as control clients.